Based On The Below Data What Is The Result Of The Regression Equation For The 15th Month?
Regression Analysis
An Innovative Arroyo to an Efficient and Constructive Financial Statements Audit
Over the last few years, nosotros have seen a trend in the financial statements inspect towards data analytics involving a 100% analysis of the population, thus allowing inspect teams to focus on the highest areas of risk whilst maintaining an efficient and effective inspect. An innovative type of information analytics is predictive modeling, including Regression Assay, which links historical analysis to hereafter performance using statistical models – an immensely powerful tool.
Introduction
In this commodity we briefly explain the cardinal concepts of regression analysis and further elaborate on how it works every bit part of a financial statements audit, covering the cardinal elements of the following phases: Planning, Model Building and Audit Interface. In addition, nosotros illustrate how these key elements take been put in practise in KPMG's Regression Analysis tool (eAAT – Account Analysis Tool) and related methodology. At the same time we summarize the advantages of using regression analysis as office of a financial statements audit equally well equally sure constraints when putting it into use.
Regression Analysis: Key Concepts
Regression analysis is a statistical technique used to predict data based on past relationships between two or more variables. The historical relationship between these variables (one dependent variable – the item we are auditing – and one or more independent variables) is mathematically divers and then practical to the electric current year's dependent variable. The expected values of the electric current yr's dependent variable are so compared to the actual values, and the significance of the differences is evaluated.
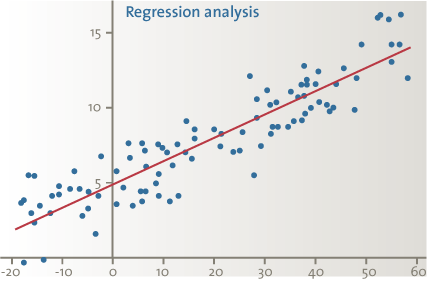
Figure ane. Regression analysis.
Example
A practical case involves a regression assay to predict the sales of a concatenation of 52 restaurants.
- The dependent variable (Y axis) is the monthly sales of each restaurant;
- The independent variable (X centrality) is the monthly amount of meat in kgs purchased past each eating place; this data is provided by the sole meat supplier for the chain of restaurants;
- Based on historical data of the last three years, a "directly line" (regression equation) is determined mathematically to be the "best fit" between the dependent (sales in euros) and the independent variable (purchased corporeality of meat in kgs);
- This regression equation based on historical data is used to predict the current yr's monthly sales of restaurants;
- The predicted monthly sales of each eating house of the chain is compared to the bodily monthly sales;
- The significance of the variances is statistically evaluated and based on the "audit interface" (see below). And so the amount or required remaining audit show (if any) is established so as to ascertain that a material misstatement does not exist relating to the completeness, existence and accuracy of the recorded sales.
How Does It Work?
Regression analysis equally part of a financial statements audit consists of iii phases: Planning – Model Building – Audit Interface.
Planning
The planning phase consists of ii types of activities:
- Determining the dependent variable (e.g., sales in euros) and the independent variable(southward) (e.m., purchased amount of meat in kgs). Note that there are 3 types of independent variables ("predictors"): financial internal predictors (eastward.g., toll of sales), non-financial internal predictors (e.g., number of clients) and external predictors (e.g., consumer cost index, purchased amount of meat in kgs).
- Collecting data: both historical data for utilise in developing a regression model, and the current year'south information.
KPMG's approach
KPMG's regression analysis tool (eAAT) involves a centralized approach, both to predefine the accounts for which the use of regression assay is suitable per industry, and to collect data for the external predictors.
Note that the reliability of the external predictors is tested centrally. For the internal predictors, the auditor needs to perform boosted procedures to decide the reliability of the data.
Model Building
This phase includes inbound the data and having a tool build the statistical model, produce the predicted values and perform a comparison with actual values.
KPMG's arroyo
A regression assay tool (eAAT) has been built centrally. This tool determines the regression model that gives the "best" predictors because correlations between an business relationship (eastward.g., sales) and its pre-defined predictors (e.yard., cost of sales).
Audit Interface
This stage consists of two activities:
- Checking the relevance and the quality of the model;
- Determining the remaining audit evidence needed.
KPMG's approach – checking the relevance and quality of the model
KPMG's arroyo includes both a quantitative and a qualitative cess to determine the relevance and quality of the model.
The quantitative cess involves determining the conviction level ensuring the account does non contain a material misstatement. The lowest level amongst all months of the current period is taken and scored on a calibration from A (highest) to F (lowest). The confidence level provides information about the predictive accurateness of the regression model.
The qualitative assessment involves determining the correlation coefficient of each predictor and rating of the quality of the source of the predictors.
- The correlation coefficient is a statistical adding that measures the force of the relationship betwixt the independent and dependent variables (varies between 0 and 1) and provides information near the relevance of the model.
- The quality of the source of the predictors is rated as follows:
- Lower: internal financial indicators from aforementioned sources (due east.one thousand., revenue and trade receivables, inventories and cost of sales)
- Moderate: internal financial information from different sources (e.thousand., revenue and toll of sales, merchandise receivables and trade payables) and internal non-financial data (east.thousand., number of employees, capacity data)
- College: external information (e.g., aggrandizement, interest rate, stock market alphabetize)
A qualitative assessment score is adamant on a scale from 1 to five, using predefined tables combining the correlation score and the type of predictor score.
eAAT after combines the Quantitative and the Qualitative scores for each account and provides a final evaluation of the audit prove obtained through the regression analysis. The scales are as follows: None, Little, Moderate, High, Extensive.
KPMG'due south approach – determining the remaining audit evidence needed
The corporeality of inspect evidence needed for substantive testing is generally determined by both the evaluation of the Inherent Take chances (Pregnant, Not Significant) and the degree of reliance on Internal Controls (Control Risk College, Control Take chances Lower). By means of some other module of eAAT (that is evaluating the client's journal entries for the period under audit by comparing actual account combinations to expected combinations), the Not Meaning Inherent Risk is further refined as follows:
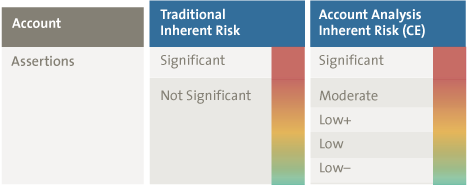
Figure 2. Refining Non Significant Inherent Take a chance.
Figure iii shows how the level of audit evidence obtained from Regression Analysis (i.e., None through Extensive) is used to determine the remaining audit testify needed for each assertion (Abyss, Existence, Accuracy and Valuation, Ownership, Presentation).
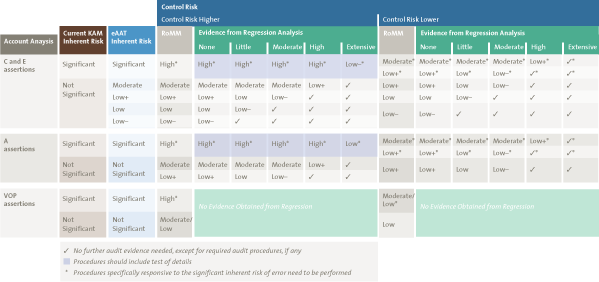
Figure 3. Determining the remaining inspect evidence needed. [Click on the epitome for a larger image]
Effigy 3 demonstrates that the refining of the Non Pregnant Inherent Risk combined with strong (Loftier, Extensive) evidence obtained from Regression Assay results in quite a number of cases where no farther testing of internal controls nor performance of additional noun testing is required. If the evidence from Regression Assay is less stiff (Fiddling, Moderate), testing of internal controls needs to be further considered simply the amount of additional substantive testing is reduced.
Also notation that if the Inherent Risk is evaluated every bit Meaning, specific substantive testing procedures demand to be performed to address the significant inherent risk of error.
In our practical case (prediction of the monthly sales of a chain of restaurants), the regression model proved to be of a high quality: a confidence level of 95% (except for 4 restaurants/months – see below), a stiff correlation (87%) and a reliable source of external data for the contained variable (a schedule of delivered amount of meat in kgs per month/restaurant provided by the sole meat supplier). Based on this, it was decided not to exam the internal controls relating to the sales procedure and to limit additional noun testing to a follow-up involving the iv restaurants/months with a confidence level of less than 95%, three of which were related to the completeness of sales and one to the beingness of sales.
Additional testing was performed, with the post-obit satisfactory results: for the three restaurants with a potential understatement of sales, it was determined that it related to new restaurants that were started up in the month, with one exception: for the one restaurant with a potential overstatement of sales, it was determined that it referred to an establishment located on the marine parade of Confirm for the month of July. For this period the boosted sales were deemed for by the increased sales of ice-cream due to the uncommonly warm weather.
Every bit a result, nosotros were able to limit the endeavour to inspect the abyss, existence and accuracy of the sales of the concatenation of restaurants to the following actions: collecting the historical and current monthly sales data (per restaurant) from the financial system and agreeing the data to the general ledger; obtaining and reviewing the annual delivery statistics (amount of meat per month/restaurant in kgs) provided past the meat supplier for the sake of reasonableness; running the regression assay and determining the quality of the model; following up on the four exceptions. The key realized efficiency was that we did not need to test the design and operating effectiveness of the sales process and of the general IT controls on the applications supporting the sales procedure. In add-on, the client was keenly interested in our innovative way of performing an audit as well every bit the possibilities of implementing a regression assay on sales as a monitoring measure by himself.
Pros and Cons of Regression Analysis
We have demonstrated in a higher place that regression analysis can be an immensely powerful tool, enabling the auditor to perform a very effective and efficient financial statements audit. If you take a model that is sufficiently stiff (High, All-encompassing), y'all just need to test the completeness and accuracy of the internal information (predictors), upload the data, and evaluate the results of the regression analysis; no further testing of internal controls nor performing of noun testing is required.
Given the higher up, combined with the fact that regression analysis is non a new statistical technique, the question arises why this technique has not been used from the beginning. The answer to this question resides partially in a number of constraints when putting it into use: customer suitability and complexity.
Client Suitability
Not all clients are suitable for regression assay every bit role of a financial statements audit. The post-obit conditions demand to be in place:
- Beingness of a repetitive transaction volume: regression analysis is not likely to exist useful in audits of clients who accept a very depression volume of transactions or when most of their individual transactions are substantial (e.g., existent estate developers, investment belongings companies);
- Availability of sufficient suitable predictors that can exist used to develop regression models: it may be a key challenge to identify predictors that result in a stiff (High, All-encompassing) model!
Typical models based on internal predictors are:
- Cost of sales to predict Revenue
- Number of customers to predict Revenue
- Revenue to predict Trade Receivables
- Head count to predict Salary Expense
- Car hours to predict Revenue
The above models may be less strong (eastward.chiliad., because only internal predictors are used) but can all the same effectively contribute to a reduction of the remaining audit testify needed.
Stronger models are likely to exist available in the case of trading and/or product companies that have a limited number of suppliers of goods/raw materials, and for which the supplier(s) can produce commitment statistics. Some examples of such external predictors are:
- The delivery statistics of nickel (provided by the nickel refinery) to predict the revenue from nickel trading;
- The delivery statistics of malt (provided past an arrangement representing the malt farmers) to predict the revenue from beer sales;
- The delivery statistics of cacao butter (provided by the primary supplier of cacao butter) to predict the revenue from chocolate sales.
Note that for the identification of both internal and external predictors, getting back to the "value chain", an old auditing technique that Dutch auditors used to be (or are) quite familiar with, may turn out to be an first-class source of inspiration.
- No new clients or clients with significant concern or system changes from prior years;
- Excluding PIEs (public interest entities) and high chance engagements.
Complexity
Another major constraint is the fact that many auditors are not or not sufficiently familiar with statistics and therefore reluctant to use regression assay every bit office of a financial statements inspect. An boosted constraint is the fear of relying on inappropriate models (e.g., autocorrelation, non-normality).
Conclusion
Regression analysis represents a very powerful tool to reduce the amount of fourth dimension spent on evaluating internal controls and/or performing substantive testing procedures for accounts with a negligible inherent risk, thus allowing auditors to focus on the higher risk areas.
The claiming is to place suitable predictors that outcome in a strong model combined with efforts to build sufficient regression analysis competence within the inspect practise and … to go neat by running a number of pilots and creating a number of success stories.
Based On The Below Data What Is The Result Of The Regression Equation For The 15th Month?,
Source: https://www.compact.nl/en/articles/regression-analysis/
Posted by: hodginwitswoompose1968.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Based On The Below Data What Is The Result Of The Regression Equation For The 15th Month?"
Post a Comment